Unleash the power of a radiant smile with a deep dive into the silent threat lurking in your mouth: Gum Disease. Beyond just a dental issue, Gum Disease can impact your overall health in ways you never imagined.
In this article, we unravel the mysteries of Gum Disease, exposing the risks and offering insights on prevention and treatment. Discover the secrets to maintaining a healthy, vibrant smile that radiates confidence.
Let’s embark on a journey to delve into the world of Gum Disease, where knowledge is not just power but also the key to unlocking a future filled with wellness and vitality.
Causes and Risk Factors of Gum Disease
Several factors contribute to the development of gum diseases, increasing an individual’s susceptibility to periodontal infections.
Poor Oral Hygiene Habits: Inadequate brushing and flossing allow plaque to accumulate along the gum line, leading to inflammation.
Tobacco Use: Smoking and tobacco consumption impair blood flow to the gums, compromising the body’s ability to fight infections.
Genetic Predisposition: Genetic factors may influence an individual’s susceptibility to gum diseases, making some people more prone to periodontal infections.
Systemic Conditions: Health conditions like diabetes and high blood pressure can weaken the immune system and exacerbate gum diseases.
Hormonal Changes: Hormonal fluctuations during puberty, pregnancy, and menopause can increase gum sensitivity and inflammation.
Symptoms and Signs of Gum Disease
Recognizing the early signs of gum diseases is crucial for timely intervention and prevention of further oral health complications.
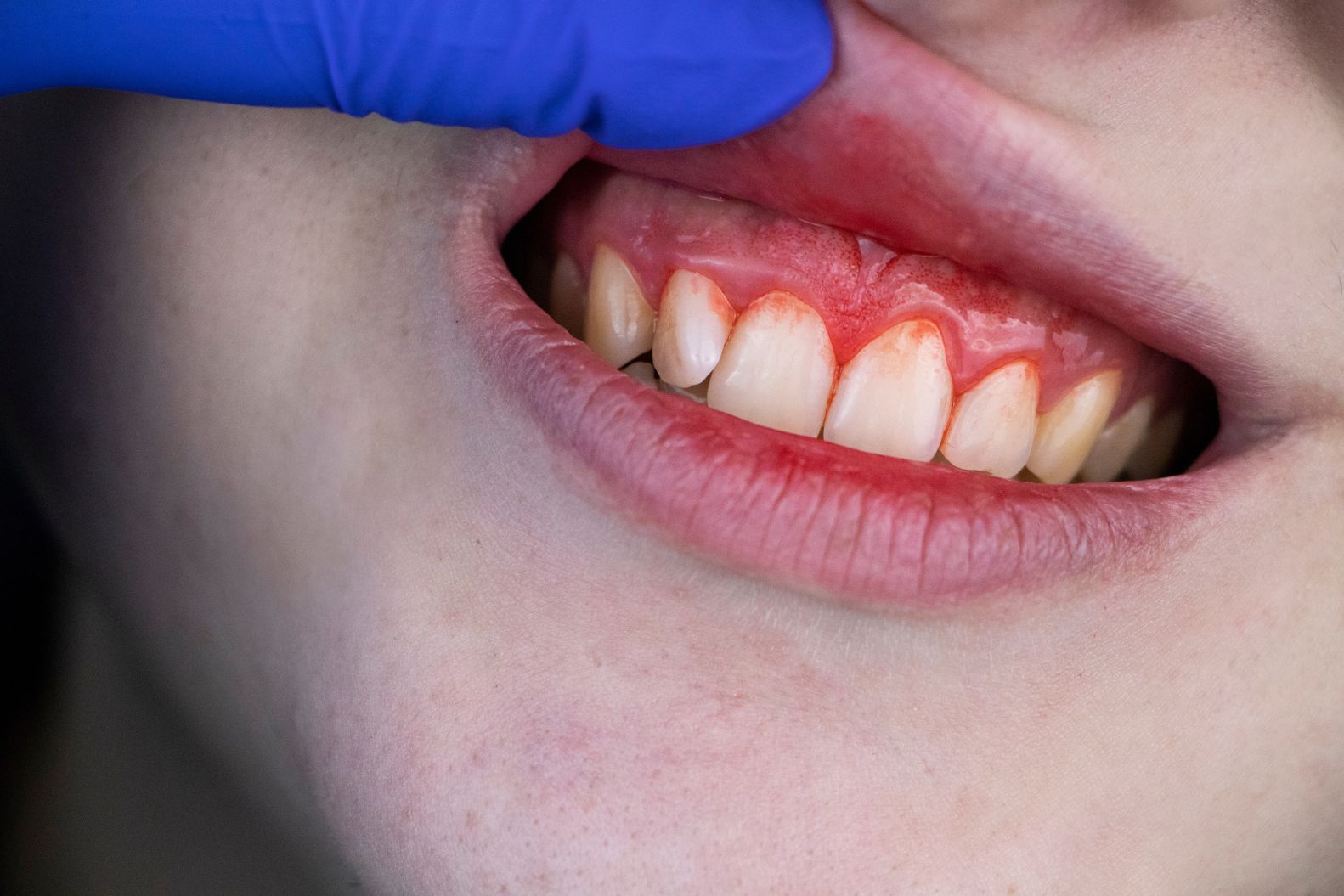
Gingivitis Symptoms: Red, swollen gums that bleed easily during brushing or flossing.
Periodontitis Symptoms: Gum recession, deep periodontal pockets, loose teeth, and persistent bad breath.
Changes in Gum Appearance: Gum inflammation, tenderness, and changes in color or texture.
Tooth Sensitivity: Increased sensitivity to hot, cold, or sweet foods due to gum recession and exposed tooth roots.
Gum Bleeding: Bleeding gums, especially during brushing or eating, may indicate gingival inflammation and early-stage gum disease.
What is the Best Treatment for Gum Disease?
Effective treatment of gum diseases involves professional interventions and proactive oral hygiene practices.
A. Non-Surgical Treatments:
Scaling and Root Planing: Deep cleaning to remove plaque and tartar buildup from below the gum line.
Antibiotic Therapy: Prescription antibiotics to target bacterial infections and reduce inflammation.
B. Surgical Interventions:
Flap Surgery: Surgical procedure to access and clean the roots of the teeth and remove diseased tissue.
Bone Grafting: Placement of bone graft material to regenerate lost bone tissue and support tooth stability.
C. Maintenance and Follow-Up Care: Regular dental visits for professional cleanings and monitoring of gum health.
Receding Gums Treatment and Prevention
Receding gums, a common complication of gum diseases, require specialized treatment to prevent further tissue loss and tooth exposure.
Gum Grafting: Surgical procedure to cover exposed tooth roots and restore gum tissue.
Proper Oral Hygiene: Brushing with a soft-bristled toothbrush and using interdental brushes or floss to clean between teeth and along the gum line.
Avoiding Aggressive Brushing: Gentle brushing techniques to prevent further gum recession and enamel erosion.
Tobacco Cessation: Quitting smoking and avoiding tobacco products to improve gum health and reduce the risk of gum diseases.
Regular Dental Check-Ups: Routine dental visits for professional cleanings and early detection of gum disease or gum recession.
What Organ does Gum Disease Affect?
Gum disease primarily affects the gums and supporting structures of the teeth, such as the periodontal ligaments and alveolar bone. However, severe cases of gum disease, particularly periodontitis, can have systemic effects and impact overall health.
Cardiovascular System:
Increased Risk of Heart Disease: The bacteria associated with gum disease can enter the bloodstream and contribute to the formation of arterial plaques, increasing the risk of heart disease, including atherosclerosis and heart attacks.
Endocarditis: In severe cases, bacteria from gum infections can travel to the heart and cause endocarditis, an inflammation of the inner lining of the heart chambers and valves.
Respiratory System:
Pneumonia: Inhalation or aspiration of oral bacteria from gum disease can lead to lung infections, such as pneumonia, particularly in individuals with compromised immune systems or respiratory conditions.
Pregnancy and Reproductive Health:
Preterm Birth and Low Birth Weight: Pregnant women with untreated gum disease are at a higher risk of preterm birth and delivering babies with low birth weight due to systemic inflammation and bacterial dissemination.
Diabetes Management:
Blood Sugar Control: Gum disease can make it more challenging to control blood sugar levels in individuals with diabetes, as systemic inflammation can interfere with insulin sensitivity and glucose metabolism.
Cognitive Health:
Alzheimer’s Disease: Emerging research suggests a potential link between chronic gum inflammation and an increased risk of Alzheimer’s disease and cognitive decline, although further studies are needed to establish causality.
Can high Blood Pressure Cause Gum Issues?
Yes, high blood pressure (hypertension) can contribute to gum issues and exacerbate existing gum diseases. Research indicates a bidirectional relationship between hypertension and gum diseases, where one condition can influence the other.
Impact on Gum Health: Hypertension can compromise the body’s immune response, making individuals more susceptible to gum infections and periodontal diseases.
Reduced Blood Flow: High blood pressure can lead to reduced blood flow to the gums, impairing their ability to heal and fight off bacterial infections.
Inflammation: Chronic inflammation associated with hypertension can exacerbate gum inflammation (gingivitis) and worsen existing gum diseases (periodontitis).
Compromised Healing: Individuals with hypertension may experience delayed wound healing, including gum tissue healing after dental procedures or treatments for gum diseases.
Systemic Health Connection: Gum diseases and hypertension share common risk factors, such as smoking, poor diet, and stress, which can further contribute to their interplay and impact on overall health.
Conclusion
Periodontal diseases pose significant risks to oral health and overall well-being if left untreated. By practicing good oral hygiene, addressing risk factors, and seeking timely dental care, individuals can preserve their gum health and reduce the risk of associated systemic conditions like high blood pressure. If you’re experiencing symptoms of gum disease or have concerns about your gum health, schedule a consultation with our dental team today. We offer comprehensive evaluations, personalized treatment plans, and expert guidance to help you achieve and maintain optimal gum health for a lifetime.
Don’t let gum disease take a toll on your oral health any longer. With our comprehensive treatment plan, you can finally bid farewell to this persistent issue. Our team of experienced dental professionals is dedicated to providing you with the care and support needed to beat gum disease once and for all. By addressing the root causes and implementing effective solutions, we ensure that you achieve a healthy and vibrant smile. Say goodbye to gum disease and hello to a brighter, healthier future with our proven approach. Let us guide you towards optimal oral health and a confident smile that lasts a lifetime.